Citation: Midtgaard, Rune. RepFocus - A Survey of the Reptiles of the World. (www.repfocus.dk).
Latest update: December 31st, 2022.






|
Genus
Hapsidophrys

 |
Emerald Snakes
|

 |
Smaragdnattern
|

 |
Afrikanske Smaragdsnoge
|

|
1856 |  |
Hapsidophrys Fischer (type species: Hapsidophrys lineatus Fischer 1856) |
|
1861 |  |
Gastropyxis Cope (type species: Dendrophis smaragdina Schlegel 1837; syn. Williams & Wallach 1989) |
|
1902 |  |
Tropidophidion Werner (type species: Dendrophis smaragdina Schlegel 1837; syn. Williams & Wallach 1989) |
Contents:
3 species, of which 1 (33.3%) is endemic.
Endemism: 0%  100% 100%
Remarks:
Zaher, Grazziotin, Cadle, Murphy, Moura-Leite & Bonatto (2009) listed Gastropyxis as a valid genus.
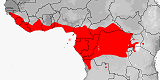
Distribution:
Equatorial Africa.
Reported from:
Angola
(incl.
Cabinda),
Benin,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Equatorial Guinea
(Bioko,
Elobey Island,
Rio Muni),
Gabon,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Guinea-Bissau,
Ivory Coast,
Kenya,
Liberia,
Nigeria,
Sao Tome & Principe
(Principe),
Sierra Leone,
Tanzania,
Togo,
Uganda.
| |

|
Hapsidophrys lineatus



 |
Black-lined Green Snake, Green-lined Snake, Striated Tree Snake, Striped Emerald Snake
|

 |
Schwarzstreifige Smaragdnatter
|

 |
Sortstribet Smaragdsnog
|

|
1856 |  |
Hapsidophrys lineatus Fischer |
|
1909 |  |
Gastropyxis orientalis Werner (Loveridge 1957) |

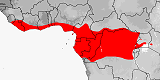
Distribution:
Benin,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Equatorial Guinea
(Bioko,
Rio Muni),
Gabon,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Ivory Coast,
Kenya,
Liberia,
Nigeria,
Sierra Leone,
South Sudan,
Tanzania,
Togo,
Uganda.
|

|

|
Hapsidophrys principis



 |
Principe Green Snake
|

 |
Principe-Smaragdnatter
|

 |
Principe-smaragdsnog
|

|
1906 |  |
Gastropyxis principis Boulenger |
|
|  |
Hapsidophrys principis Jesus, Nagy, Branch, Wink, Brehm & Harris 2009 |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a synomym of smaragdina.
Revalidated by Lawson, Slowinski, Crother & Burbrink (2005) and Jesus, Nagy, Branch, Wink, Brehm & Harris (2009), although also Manacas (1956) treated it as a valid species.
Chippaux & Jackson (2019) claimed the species to be present in Sao Thome, but no localities were shown in the island in their map.
The record is considered erroneous, since no other references have been found to support their claim.
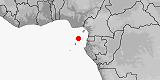
Distribution:
Sao Tome & Principe
(Principe).
|

|

|
Hapsidophrys smaragdinus



 |
Common Emerald Snake, Keel-scaled Green Snake
|

 |
Kielschuppige Smaragdnatter
|

 |
Kølskællet Smaragdsnog
|

|
1837 |  |
Dendrophis smaragdina Schlegel |
|
|  |
Leptophis smaragdinus Hallowell 1854 |
|
|  |
Gastropyxis smaragdina Cope 1860 |
|
|  |
Hapsidophrys smaragdinus Bocage 1895 |
|
1844 |  |
Leptophis gracilis Hallowell (Loveridge 1957) |
|
1856 |  |
Hapsidophrys caeruleus Fischer (Loveridge 1957) |

Remarks:
Previously included principis. Records from Principe refer to principis.
Records from Gambia (e.g., Håkansson 1981, Gruschwitz, Lenz & Böhme 1991) are probably based on misidentified
Philothamnus irregularis or
Philothamnus semivariegatus (Trape & Mané 2006a).
Records from Sao Tome are regarded as erroneous (Ceríaco, Marques & Bauer 2018).
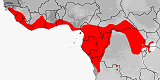
Distribution:
Angola
(incl.
Cabinda),
Benin,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Equatorial Guinea
(Bioko,
Elobey Island,
Rio Muni),
Gabon,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Guinea-Bissau,
Ivory Coast,
Liberia,
Nigeria,
Sierra Leone,
Tanzania,
Togo,
Uganda.
|

|
|