Citation: Midtgaard, Rune. RepFocus - A Survey of the Reptiles of the World. (www.repfocus.dk).
Latest update: December 31st, 2022.






|
Genus
Pantherophis

 |
North American Rat Snakes, (Racers)
|

 |
Nordamerikanische Kletternattern
|

 |
Nordamerikanske Rottesnoge
|

|
1843 |  |
Pantherophis Fitzinger (type species: Coluber guttatus Linnaeus 1766) |
|
1853 |  |
Scotophis Baird in Baird & Girard (type species: Scotophis alleghaniensis Holbrook 1836) |
|
2008 |  |
Mintonius Collins & Taggart (type species: Scotophis vulpinus Baird & Girard 1853) |
Contents:
8 species, of which 4 (50.0%) are endemic.
Endemism: 0%  100% 100%
Remarks:
Previously included in the genus
Elaphe (e.g., Schulz 1996).
Revalidated by Utiger, Helfenberger, Schätti, Schmidt, Ruf & Ziswiler (2002). Scotophis was recognized as a valid genus by Collins & Taggart (2008).
Hillis (2022) suggested a different taxonomy for members of the P. obsoletus complex.
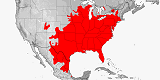
Distribution:
E. and C. North America.
Reported from:
Canada
(Ontario),
Mexico
(Aguascalientes,
Chihuahua,
Coahuila,
Durango,
Hidalgo,
Nuevo Leon,
Queretaro,
San Luis Potosi,
Tamaulipas,
Veracruz),
USA
(Alabama,
Arkansas,
Colorado,
Connecticut,
Delaware,
Florida,
Georgia,
Illinois,
Indiana,
Iowa,
Kansas,
Kentucky,
Louisiana,
Maryland,
Massachusetts,
Michigan,
Minnesota,
Mississippi,
Missouri,
Nebraska,
New Jersey,
New Mexico,
New York,
North Carolina,
Ohio,
Oklahoma,
Pennsylvania,
Rhode Island,
South Carolina,
South Dakota,
Tennessee,
Texas,
Utah,
Vermont,
Virginia,
Washington, D.C.,
West Virginia,
Wisconsin).
| |

|
Pantherophis alleghaniensis



 |
Grey Rat Snake, Central Rat Snake
|

 |
Graue Kletternatter
|

 |
Grå Rottesnog
|

|
1836 |  |
Scotophis alleghaniensis Holbrook |
|
|  |
Elaphis alleghaniensis Hallowell 1856 |
|
|  |
Elaphe alleghaniensis Burbrink 2001 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis alleghaniensis Christensen 2008 |
|
|  |
Scotophis alleghaniensis Collins & Taggart 2008 |
|
1854 |  |
Elaphis spiloides Dumeril, Bibron & Dumeril (syn. Hillis & Wüster 2021) |
|
|  |
Coluber obsoletus spiloides Cope 1888 |
|
|  |
Elaphe obsoleta spiloides Dowling 1952 |
|
|  |
Elaphe spiloides Burbrink 2001 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis obsoletus spiloides Schmidt & Kunz 2005 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis spiloides Crother, Boundy, Burbrink & Campbell in Crother (ed.) 2008 |
|
|  |
Scotophis spiloides Collins & Taggart 2008 |
|
1888 |  |
Coluber obsoletus lemniscatus Cope [part] (syn. Hillis & Wüster 2021, by implication) |

Remarks:
Previously referred to as spiloides.
Formerly regarded as a synonym of obsoletus (e.g., Dowling 1952).
Revalidated as a separate species by Burbrink (2001) [as spiloides].
Hillis & Wüster (2021) clarified the taxonomy of this and related species.
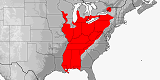
Distribution:
Canada
(Ontario),
USA
(Alabama,
Arkansas,
Florida,
Georgia,
Illinois,
Indiana,
Kentucky,
Louisiana,
Michigan,
Mississippi,
Missouri,
New York,
Ohio,
Pennsylvania,
Tennessee,
West Virginia,
Wisconsin).
|

|

|
Pantherophis bairdi



 |
Rio Grande Rat Snake, (Baird's Rat Snake)
|

 |
Rio-Grande-Kletternatter
|

 |
Rio Grande-rottesnog, (Bairds Rottesnog)
|

|
1880 |  |
Coluber bairdi Yarrow |
|
|  |
Elaphe bairdi Stejneger & Barbour 1917 |
|
|  |
Elaphe obsoleta bairdi Dowling 1952 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis bairdi Utiger, Helfenberger, Schätti, Schmidt, Ruf & Ziswiler 2002 |
|
|  |
Scotophis bairdi Collins & Taggart 2008 |

Remarks:
Revalidated as a separate species by Olson (1977).
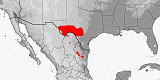
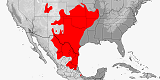
Distribution:
Mexico
(Coahuila,
Nuevo Leon,
Tamaulipas),
USA
(Texas).
|


Pantherophis bairdi
© Rune Midtgaard
|

|
Pantherophis emoryi



 |
Great Plains Rat Snake
|

 |
Prärie-Kornnatter
|

 |
Prærie-rottesnog
|

|
1853 |  |
Scotophis emoryi Baird & Girard |
|
|  |
Coluber emoryi Cope 1886 |
|
|  |
Elaphe emoryi Dowling 1951 |
|
|  |
Elaphe guttata emoryi Dowling 1952 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis emoryi Potts & Collins 2005 |
|
1859 |  |
Scotophis calligaster Kennicott (Burbrink 2002) |
|
1860 |  |
Coluber rhinomegas Cope (Schmidt 1953; Burbrink 2002) |
|
1942 |  |
Elaphe laeta intermontanus Woodbury & Woodbury (Schmidt 1953; Burbrink 2002) |
|
1994 |  |
Elaphe guttata meahllmorum Smith, Chiszar, Staley & Tepedelen (Burbrink 2002) |
|
|  |
Pantherophis emoryi meahllmorum Lemos-Espinal & Smith 2007 |
|
2002 |  |
Elaphe slowinskii Burbrink (syn. Marshall, Chambers, Matz & Hillis 2021) |
|
|  |
Pantherophis slowinskii Jiang, Castoe, Austin, Burbrink, Herron, McGuire, Parkinson & Pollock 2007 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis emoryi slowinskii Marshall, Chambers, Matz & Hillis 2021 |

Other common names:
meahllmorum: Southwestern Ratsnake
slowinskii: Kisatchie Corn Snake, (Slowinski's Corn Snake)
Remarks:
Revalidated as a separate species by Burbrink (2002).
The taxon meahllmorum is considered either a synonym (e.g., Burbrink 2002) or a subspecies (e.g., Lemos-Espinal & Smith 2007; Marshall, Chambers, Matz & Hillis 2021) of emoryi.
In older literature (e.g., Boulenger 1894; Stejneger & Barbour 1917, 1943), emoryi was referred to under the name laeta, which later (Dowling 1951) was shown to be a synonym
of obsoletus.
Not mentioned for Queretaro by Cruz-Elizalde, Ramírez-Bautista, Hernández-Salinas, Berriozabal-Islas & Wilson (2019).
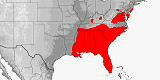
Distribution:
Mexico
(Aguascalientes,
Chihuahua,
Coahuila,
Durango,
Guanajuato,
Hidalgo,
Nuevo Leon,
San Luis Potosi,
Tamaulipas,
Veracruz),
USA
(Arkansas,
Colorado,
Illinois,
Kansas,
Louisiana,
Missouri,
Nebraska,
New Mexico,
Oklahoma,
Texas,
Utah).
|

|

|
Pantherophis guttatus



 |
Red Corn Snake
|

 |
Rote Kornnatter, Kornnatter
|

 |
Rød Kornsnog
|

|
1766 |  |
Coluber guttatus Linnaeus |
|
|  |
Elaphis guttatus Duméril, Bibron & Duméril 1854 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis guttatus Utiger, Helfenberger, Schätti, Schmidt, Ruf & Ziswiler 2002 |
|
1790 |  |
Coluber maculatus Bonnaterre (Smith, Chiszar, Staley & Tepedlen 1994; Burbrink 2002) |
|
1802 |  |
Coluber carolinianus Shaw (Schmidt 1953; Schwartz & Henderson 1988; Burbrink 2002) |
|
1820 |  |
Coluber pantherinus Merrem (Schmidt 1953; Burbrink 2002) |
|
1827 |  |
Coluber floridanus Harlan (Schmidt 1953; Burbrink 2002) |
|
1888 |  |
Coluber guttatus sellatus Cope (Schmidt 1953; Burbrink 2002) |
|
1888 |  |
Coluber rosaceus Cope (Burbrink 2002) |
|
|  |
Elaphe rosacea Barbour 1920 |
|
|  |
Elaphe guttata rosacea Neill 1949 |

Other common names:
rosacea: Rosy Rat Snake
Remarks:
Previously included emoryi.
Introduced to:
Anguilla
(Anguilla Island),
Antigua & Barbuda
(Antigua),
Bahamas
(Little Bahama Bank),
Brazil
(Bahia),
British Virgin Islands,
Cayman Islands
(Grand Cayman),
Martinique,
Saint Barthelemy,
Saint Martin,
South Africa
(Eastern Cape,
Gauteng,
KwaZulu-Natal,
Western Cape),
Turks & Caicos Islands
(Turks Islands),
U.S. Virgin Islands
(St. Croix).
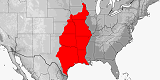
Distribution:
USA
(Alabama,
Arkansas,
Delaware,
Florida,
Georgia,
Kentucky,
Louisiana,
Maryland,
Mississippi,
New Jersey,
North Carolina,
Pennsylvania,
South Carolina,
Tennessee,
Texas,
Virginia,
Washington, D.C.,
West Virginia).
|


Pantherophis guttatus
© Rune Midtgaard
|

|
Pantherophis obsoletus



 |
Western Rat Snake
|

 |
Westamerikanische Erdnatter, Kükennatter, (Erdnatter)
|

 |
Vestamerikansk Rottesnog
|

|
1823 |  |
Coluber obsoletus Say |
|
|  |
Elaphis obsoletus Garman 1883 |
|
|  |
Elaphe obsoleta Stejneger & Barbour 1917 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis obsoletus Utiger, Helfenberger, Schätti, Schmidt, Ruf & Ziswiler 2002 |
|
|  |
Scotophis obsoletus Collins & Taggart 2008 |
|
1853 |  |
Scotophis laetus Baird & Girard (Dowling 1951; Burbrink 2001) |
|
|  |
Elaphe laeta Stejneger & Barbour 1917 |
|
1853 |  |
Scotophis lindheimeri Baird & Girard (Burbrink 2001) |
|
|  |
Elaphis obsoletus lindheimerii Garman 1883 |
|
|  |
Coluber obsoletus lindheimeri Brown 1901 |
|
|  |
Elaphe obsoleta lindheimeri Stejneger & Barbour 1917 |

Other common names:
lindheimeri: Texas Rat Snake
obsoleta: Black Rat Snake
Remarks:
Previously included alleghaniensis and quadrivittatus.
Introduced to:
USA
(Florida).
Distribution:
USA
(Arkansas,
Iowa,
Kansas,
Louisiana,
Minnesota,
Missouri,
Nebraska,
Oklahoma,
Texas).
|

|

|
Pantherophis quadrivittatus



 |
Eastern Rat Snake, (Black Rat Snake, Pilot Black Snake, Chicken Snake)
|

 |
Ostamerikanische Erdnatter
|

 |
Østamerikansk Rottesnog, Sort Rottesnog, Gul Rottesnog (quadrivittatus), Orange Rottesnog (rossalleni)
|

|
1836 |  |
Coluber quadrivittatus Holbrook |
|
|  |
Elaphis quadri-vittatus Duméril, Bibron & Duméril 1854 |
|
|  |
Elaphe obsoleta quadrivittata Neill 1949 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis quadrivittata Hillis & Wüster 2021 |
|
1853 |  |
Scotophis confinis Baird & Girard (Burbrink 2001, by implication) |
|
1854 |  |
Elaphis holbrookii Duméril, Bibron & Duméril (Wallach, Williams & Boundy 2014) |
|
1888 |  |
Coluber obsoletus lemniscatus Cope [part] (Burbrink 2001, by implication) |
|
1932 |  |
Elaphe quadrivittata deckerti Brady (Burbrink 2001, by implication) |
|
1949 |  |
Elaphe obsoleta rossalleni Neill (Burbrink 2001, by implication) |
|
1940 |  |
Elaphe williamsi Barbour & Carr (Burbrink 2001, by implication) |
|
1942 |  |
Elaphe quadrivittata parallela Barbour & Engels (Burbrink 2001, by implication) |

Other common names:
quadrivittata: Yellow Rat Snake
rossalleni: Everglades Rat Snake
williamsi: Gulf Hammock Rat Snake
Remarks:
Previously referred to as alleghaniensis (e.g., Burbrink 2001).
Formerly regarded as a synonym of obsoletus (e.g., Schmidt 1953).
Revalidated as a separate species by Burbrink (2001) [as alleghaniensis].
Hillis & Wüster (2021) clarified the taxonomy of this and related species.
Introduced to:
Bahamas
(Little Bahama Bank),
Martinique,
South Africa
(Gauteng).
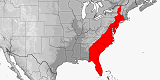
Distribution:
USA
(Connecticut,
Delaware,
Florida,
Georgia,
Kentucky,
Maryland,
Massachusetts,
New Jersey,
New York,
North Carolina,
Pennsylvania,
Rhode Island,
South Carolina,
Vermont,
Virginia,
Washington, D.C.).
|


Pantherophis quadrivittatus
© Rune Midtgaard
|

|
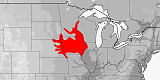
Pantherophis ramspotti



 |
Western Fox Snake
|

 |
Westliche Fuchsnatter
|

 |
Vestlig Rævesnog
|

|
2011 |  |
Pantherophis ramspotti Crother, White, Savage, Eckstut, Graham & Gardner |

Remarks:
This species corresponds to the western half of the populations of the former understanding of vulpina (see remarks there).
Distribution:
USA
(Iowa,
Minnesota,
Missouri,
Nebraska,
South Dakota).
|

|

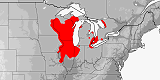
|
Pantherophis vulpinus



 |
Eastern Fox Snake (previously known as Western Fox Snake, see remarks)
|

 |
Östliche Fuchsnatter
|

 |
Østlig Rævesnog
|

|
1853 |  |
Scotophis vulpinus Baird & Girard |
|
|  |
Elaphe vulpinus Ruthven 1909 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis vulpinus Utiger, Helfenberger, Schätti, Schmidt, Ruf & Ziswiler 2002 |
|
|  |
Mintonius vulpinus Collins & Taggart 2008 |
|
1854 |  |
Elaphe rubriceps Duméril, Bibron & Duméril (Schmidt 1953) |
|
1940 |  |
Elaphe vulpina gloydi Conant (Crother, White, Savage, Eckstut, Graham & Gardner 2011) |
|
|  |
Elaphe gloydi Collins 1991 |
|
|  |
Pantherophis gloydi Schmidt & Kunz 2005 |
|
|  |
Mintonius gloydi Collins & Taggart 2008 |

Remarks:
Crother, White, Savage, Eckstut, Graham & Gardner (2011) redefined species limits and distributions within the vulpina/gloydi/ramspotti group. They showed that the type specimens of vulpina and gloydi belong to the same form. However, their studies also showed that snakes from the western half of the distribution of the species until then known as the Western Fox Snake (vulpina) represented a separate species, which they described as ramspotti. Consequently, ramspotti corresponds to the western half of the former concept of vulpina, whereas the current vulpina corresponds to the eastern half of the populations of the former vulpina as well as the taxon formerly known as gloydi.
Distribution:
Canada
(Ontario),
USA
(Illinois,
Indiana,
Michigan,
Missouri,
Ohio,
Wisconsin).
|

|
|