|
Genera
 | |
|
|
Citation: Midtgaard, Rune. RepFocus - A Survey of the Reptiles of the World. (www.repfocus.dk).
Latest update:
January 1st, 2025.
Teiidae

Greater Tejus
 Schienenechsen
Schienenechsen
 Stortejuer
Stortejuer
|
Contents:
| Endemicity:
| |
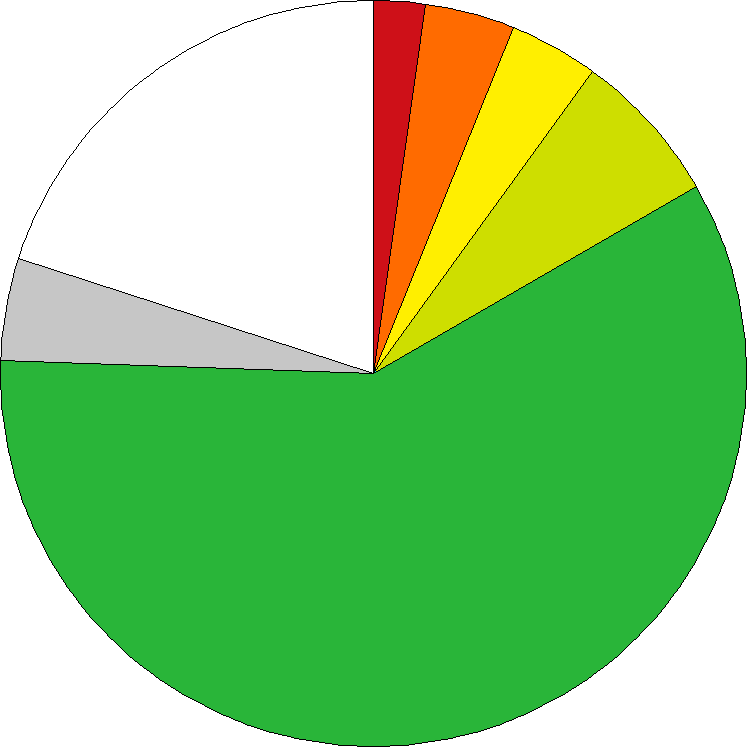
18 genera of which 2 (11.1%) are endemic | 0%  100% 100%
| |
179 species of which 107 (59.8%) are endemic | 0%  100% 100%
|
In addition to this, 2 species have been described based on laboratory hybridizations (see
Aspidoscelis neavesi and
A. priscillae.
Remarks:
Previously included the subfamily Gymnophthalminae, now the family
Gymnophthalmidae. Presch (1973) divided the family Teiidae (in the traditional sense) into two separate families, Teiidae (in the strict sense, comprising the genera
Ameiva,
Aspidoscelis (revalidated subsequently),
Callopistes,
Cnemidophorus,
Crocodilurus,
Dicrodon,
Dracaena,
Kentropyx,
Teius,
Tupinambis) and
Gymnophthalmidae (comprising the remaining genera).
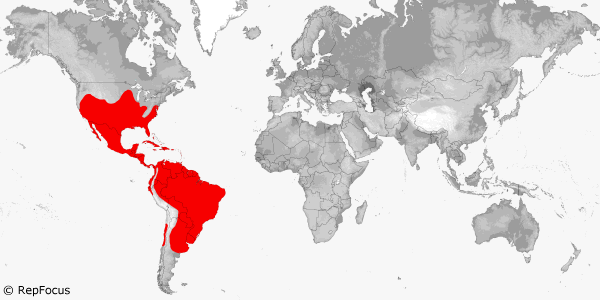
Distribution:
North America, Central America, South America, West Indies.
Reported from:
Anguilla,
Antigua & Barbuda,
Argentina,
Aruba,
Bahamas,
Barbados,
Belize,
Bolivia,
Bonaire,
Brazil,
British Virgin Islands,
Chile,
Colombia,
Costa Rica,
Cuba,
Curacao,
Dominica,
Dominican Republic,
Ecuador,
El Salvador,
French Guiana,
Grenada,
Guatemala,
Guyana,
Haiti,
Honduras,
Jamaica,
Martinique,
Mexico,
Montserrat,
Nicaragua,
Panama,
Paraguay,
Peru,
Puerto Rico,
Saint Barthelemy,
Saint Kitts & Nevis,
Saint Lucia,
Saint Martin,
Saint Vincent & the Grenadines,
Sint Eustatius,
Surinam,
Trinidad & Tobago,
U.S. Virgin Islands,
Uruguay,
USA,
Venezuela.
|
|








|
|