Citation: Midtgaard, Rune. RepFocus - A Survey of the Reptiles of the World. (www.repfocus.dk).
Latest update:
August 27th, 2024.






|
Genus
Panaspis

 |
African Snake-eyed Skinks, African Lidless Skinks
|

 |
Afrikanische Natternaugen
|

 |
Afrikanske Brilleskinker
|

|
1868 |  |
Panaspis Cope (type species: Panaspis aeneus Cope 1868) |
|
1974 |  |
Afroablepharus Greer (type species: Cryptoblepharus walbergii Smith 1849; syn. Medina, Bauer, Branch, Schmitz, Conradie, Nagy, Hibbitts, Ernst, Portik, Nielsen, Colston, Kusamba, Behangana, Rödel & Greenbaum 2016) |
Contents:
22 species, of which 13 (59.1%) are endemic.
Endemism: 0%  100% 100%
Remarks:
Previously included
Leptosiaphos.
Afroablepharus was previously regarded as a synonym of Panaspis (e.g., Broadley 1989), then as a valid genus, and most recently again as a synonym of Panaspis.
Two species (africanus, annobonensis) are included in Panaspis on the basis of Schmitz, Ineich & Chirio (2005) and Jesus, Harris & Brehm (2007),
who placed these two species in Afroablepharus, despite the absence of an ablepharine eye ("snake-eye") characteristic of the remaining species of the genus.
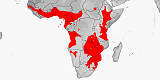
Distribution:
SubSaharan Africa.
Reported from:
Angola
(incl.
Cabinda),
Benin,
Botswana,
Burkina Faso,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Chad,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Equatorial Guinea
(Annobon,
Bioko,
Rio Muni),
Eswatini,
Ethiopia,
Gabon,
Gambia,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Guinea-Bissau,
Ivory Coast,
Kenya,
Malawi,
Mali,
Mozambique
(incl.
Bazaruto Archipelago
[Benguerua]),
Namibia,
Niger,
Nigeria,
Sao Tome & Principe
(Principe,
Rolas Island,
Santana Islet,
Sao Tome),
Senegal,
Somalia,
South Africa
(Eastern Cape,
Free State,
Gauteng,
KwaZulu-Natal,
Limpopo,
Mpumalanga,
North West Province,
Northern Cape),
Sudan,
Tanzania,
Togo.
Uganda,
Zambia,
Zimbabwe.
| |

|
Panaspis africanus



 |
Principe Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Principe-Natternauge
|

 |
Principe-brilleskink
|

|
1845 |  |
Mocoa africana Gray |
|
|  |
Lygosoma africanum Peters 1874 |
|
|  |
Riopa africanum Smith 1937 |
|
|  |
Leiolopisma africana Mittleman 1952 |
|
|  |
Panaspis africana Fuhn 1972 |
|
|  |
Leptosiaphos africana Haft 1993 |
|
|  |
Afroablepharus africanus Jesus, Harris & Brehm 2007 |

Remarks:
Previously included annobonensis and the population now assigned to thomensis.
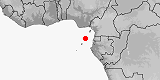
Distribution:
Sao Tome & Principe
(Principe).
|

|

|
Panaspis annettesabinae



 |
Oromia Snake-eyed Skink, (Sabin's Snake-Eyed Skink)
|

 |
Oromia-Natternauge
|

 |
Oromia-brilleskink
|

|
2020 |  |
Panaspis annettesabinae Colston, Pyron & Bauer |

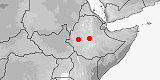
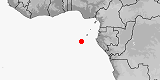
Distribution:
Ethiopia.
|

|

|
Panaspis annobonensis



 |
Annobon Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Annobon-Natternauge
|

 |
Annobon-brilleskink
|

|
1972 |  |
Panaspis africana annobonensis Fuhn |
|
|  |
Panaspis annobonensis Perret 1973 |
|
|  |
Leptosiaphos annobonensis Broadley 1989 |
|
|  |
Afroablepharus annobonensis Jesus, Harris & Brehm 2007 |

Remarks:
Validity as a separate species confirmed by Soares, Ceríaco, Marques, Bastos-Silveira, Scheinberg, Harris, Brehm & Jesus (2018).
Distribution:
Equatorial Guinea
(Annobon).
|

|


|
Panaspis breviceps



 |
Short-headed Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Kurzkopf-Natternauge
|

 |
Korthovedet Brilleskink
|

|
1873 |  |
Euprepes breviceps Peters |
|
|  |
Lygosoma breviceps Boulenger 1887 |
|
|  |
Riopa breviceps Smith 1937 |
|
|  |
Panaspis breviceps Mittleman 1952 |
|
|  |
Leptosiaphos breviceps Broadley 1989 |
|
1900 |  |
Mabuia batesi Boulenger (Fuhn 1972) |
|
1909 |  |
Lygosoma buchneri Werner (Fuhn 1972) |
|
1917 |  |
Lygosoma auricillatum Chabanaud (Fuhn 1972) |

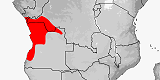
Distribution:
Angola,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Equatorial Guinea
(Bioko,
Rio Muni),
Gabon,
Nigeria.
|

|

|
Panaspis cabindae



 |
Cabinda Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Cabinda-Natternauge
|

 |
Cabinda-brilleskink
|

|
1866 |  |
Ablepharus cabindae Bocage |
|
|  |
Riopa cabindae Smith 1937 |
|
|  |
Panaspis cabindae Mittleman 1952 |
|
1868 |  |
Panaspis aeneus Cope (Fuhn 1970) |

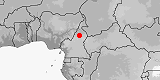
Distribution:
Angola
(incl.
Cabinda),
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa.
|

|

|
Panaspis duruarum



 |
Cameroon Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Kamerunisches Natternauge
|

 |
Camerounsk Brilleskink
|

|
1949 |  |
Ablepharus duruarum Monard |
|
|  |
Panaspis duruarum Fuhn 1969 |
|
|  |
Afroablepharus duruarus Greer 1974 |

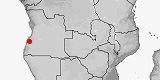
Distribution:
Cameroon.
|

|

|
Panaspis ericae



 |
Catchi Snake-eyed Skink, (Erica's Snake-Eyed Skink)
|

 |
Catchi-Natternauge
|

 |
Catchi-brilleskink
|

|
2024 |  |
Panaspis ericae Marques, Parrinha, Lopes-Lima, Tiutenko, Bauer & CerÃaco |

Distribution:
Angola.
|

|

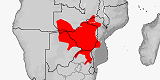
|
Panaspis maculicollus



 |
Spotted-neck Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Halsfleckiges Natternauge
|

 |
Halsplettet Brilleskink
|

|
2000 |  |
Panaspis maculicollus Jacobsen & Broadley |

Distribution:
Angola,
Botswana,
Malawi,
Mozambique,
Namibia,
South Africa
(Limpopo,
Mpumalanga),
Zambia,
Zimbabwe.
|

|

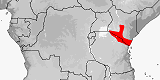
|
Panaspis massaiensis



 |
Masai Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Masai-Natternauge
|

 |
Masai-brilleskink
|

|
1924 |  |
Ablepharus massaiensis Angel |
|
|  |
Panaspis massaiensis Kilunda, Conradie, Wasonga, Jin, Peng, Murphy, Malonza & Che 2019 |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a synonym of wahlbergii (e.g., Fuhn 1970).
Revalidated as a separate species by Kilunda, Conradie, Wasonga, Jin, Peng, Murphy, Malonza & Che (2019).
Distribution:
Kenya.
|

|

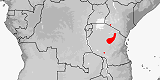
|
Panaspis megalurus



 |
Tanzanian Blue-tailed Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Tansanianisches Blauschwanz-Natternauge
|

 |
Tanzaniansk Blåhalet Brilleskink
|

|
1913 |  |
Ablepharus megalurus Nieden |
|
|  |
Panaspis megalurus Fuhn 1970 |
|
|  |
Afroablepharus megalurus Greer 1974 |

Remarks:
Jacobsen & Broadley (2000) erroneously stated that megalurus is known only from the Sudan.
The authors presumably had wilsoni in mind.
Distribution:
Ethiopia,
Kenya,
Tanzania.
|

|


|
Panaspis mocamedensis



 |
Moçamedes Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Moçamedes-Natternauge
|

 |
Moçamedes-brilleskink
|

|
2020 |  |
Panaspis mocamedensis Ceríaco, Heinicke, Parker, Marques & Bauer |

Distribution:
Angola.
|

|

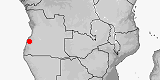
|
Panaspis mundavambo



 |
Serra da Neve Snake-Eyed Skink
|

 |
Serra-da-Neve-Natternauge
|

 |
Serra da Neve-brilleskink
|

|
2024 |  |
Panaspis mundavambo Marques, Parrinha, Lopes-Lima, Tiutenko, Bauer & CerÃaco |

Distribution:
Angola.
|

|

|
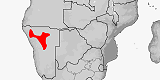
Panaspis namibiana



 |
Namibian Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Namibianisches Natternauge
|

 |
Namibiansk Brilleskink
|

|
2018 |  |
Panaspis namibiana Ceríaco, Branch & Bauer |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a population of wahlbergii.
Distribution:
Namibia.
|

|

|
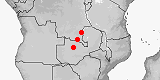
Panaspis seydeli



 |
Congolese Snake-eyed Skink, (Seydel's Snake-eyed Skink)
|

 |
Kongolesisches Natternauge
|

 |
Congolesisk Brilleskink
|

|
1933 |  |
Ablepharus seydeli Witte |
|
|  |
Panaspis seydeli Broadley & Cotterill 2004 |
|
1933 |  |
Ablepharus moeruensis Witte |
|
1955 |  |
Ablepharus anselli Fitzsimons (Largen & Spawls 2010, by implication) |

Other common names:
smithi: Upempa Snake-eyed Skink
Remarks:
Regarded as a synonym of tancredii by Broadley (1989), but as a separate species by Fuhn (1970) and Largen & Spawls (2010, by implication).
Previously included smithi.
Distribution:
Congo-Kinshasa,
Zambia.
|

|

|
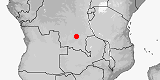
Panaspis smithi



 |
Upemba Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Upemba-Natternauge
|

 |
Upemba-brilleskink
|

|
1936 |  |
Ablepharus smithi De Witte |
|
|  |
Panaspis smithi Broadley 1989 |

Remarks:
Regarded by some authors as a synonym of seydeli (e.g., Ceríaco, Branch & Bauer 2018 [by implication]).
The Reptile Database consider smithi 'readily distinguished' from seydeli, based on pers. comm. with the late D.G. Broadley, however, they still list it as a synonym of seydeli,
presumably pending a formal revalidation of smithi.
It is tentatively considered a valid species herein, following Broadley (1989).
Distribution:
Congo-Kinshasa.
|

|

|
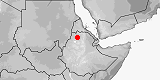
Panaspis tancredii



 |
Dabarif Snake-eyed Skink, (Ethiopian Snake-eyed Skink)
|

 |
Dabarif-Natternauge
|

 |
Dabarif-brilleskink
|

|
1909 |  |
Ablepharus tancredii Boulenger |
|
|  |
Panaspis tancredii Fuhn 1970 |
|
|  |
Afroablepharus tancredi Greer 1974 |

Remarks:
Previously included seydeli (e.g., Broadley 1989), but regarded by Fuhn (1970) and by Largen & Spawls (2010) as a separate species. According to the latter authors, tancredii is known only from a single Ethiopian specimen. Fuhn's (1970) record from Zambia refer to anselli, here consequently regarded as a synonym of seydeli. All other records of tancredii from outside Ethiopia are herein also tentatively referred to seydeli.
Distribution:
Ethiopia.
|

|

|
Panaspis thomensis



 |
São Tomé Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
São-Tomé-Natternauge
|

 |
São Tomé-brilleskink
|

|
2018 |  |
Panaspis thomensis Soares, Ceríaco, Marques, Bastos-Silveira, Scheinberg, Harris, Brehm & Jesus |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a population of africanus.
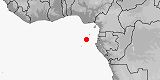
Distribution:
São Tomé & Príncipe
(São Tomé,
incl.
Rolas Island
and
Santana Islet).
|

|

|
Panaspis togoensis



 |
Togo Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Togo-Natternauge
|

 |
Togoansk Brilleskink
|

|
1902 |  |
Lygosoma togoense Werner |
|
|  |
Riopa togoense Smith 1937 |
|
|  |
Panaspis togoensis Mittleman 1952 |
|
|  |
Panaspis breviceps togoensis Grandison 1956 |
|
|  |
Lygosoma breviceps togoense Loveridge 1952 |
|
|  |
Leptosiaphos togoensis Broadley 1989 |
|
1913 |  |
Lygosoma kitsoni Boulenger (Barbault 1974; Perret 1975) |
|
1916 |  |
Lygosoma houyi Sternfeld (Schmitz, Ineich & Chirio & 2005) |
|
1917 |  |
? Lygosoma spurrelli Boulenger (Loveridge 1952) |
|
1917 |  |
Lygosoma dahomeyense Chabanaud (Loveridge 1952) |

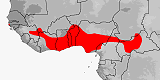
Distribution:
Benin,
Burkina Faso,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Chad,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Ivory Coast,
Mali,
Niger,
Nigeria,
Senegal,
Togo.
|

|

|
Panaspis tristaoi



 |
Nimba Snake-eyed Skink, (Tristao's Lidless Skink)
|

 |
Nimba-Natternauge
|

 |
Nimba-brilleskink
|

|
1940 |  |
Riopa tristaoi Monard |
|
|  |
Panaspis tristaoi Trape, Trape & Chirio 2012 |
|
1944 |  |
Lygosoma nimbense Angel (Trape, Trape & Chirio 2012) |
|
|  |
Panaspis nimbense Mittleman 1952 |
|
|  |
Leptosiaphos nimbensis Broadley 1989 |
|
|  |
Panaspis nimbaense [sic] Ceríaco, Branch & Bauer 2018 |

Remarks:
Previously (as nimbense) regarded as a synonym of togoensis (e.g., Loveridge 1952).
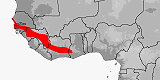
Distribution:
Gambia,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Guinea-Bissau,
Ivory Coast,
Senegal.
|

|

|
Panaspis tsavoensis



 |
Tsavo Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Tsavo-Natternauge
|

 |
Tsavo-brilleskink
|

|
2019 |  |
Panaspis tsavoensis Kilunda, Conradie, Wasonga, Jin, Peng, Murphy, Malonza & Che |

Distribution:
Kenya.
|

|


|
Panaspis wahlbergii



 |
Savanna Snake-eyed Skink, (Wahlberg's Snake-eyed Skink, Wahlberg's Dwarf Skink)
|

 |
Savannen-Natternauge
|

 |
Savanne-brilleskink
|

|
1849 |  |
Cryptoblepharus walbergii Smith |
|
|  |
Ablepharus wahlbergii Peters 1882 |
|
|  |
Panaspis wahlbergii Fuhn 1970 |
|
|  |
Afroablepharus wahlbergi Greer 1974 |
|
1894 |  |
Ablepharus carsonii Boulenger (Fuhn 1970) |

Remarks:
According to Malonza & Bwong (2023) now restricted to South Africa, but taxonomy of populations from other countries is not fully resolved.
Previously included massaiensis and the populations now assigned to maculicollus, namibiana, and tsavoensis.
Older records of wahlbergii from Namibia refer to maculicollus and namibiana (Jacobsen & Broadley 2000; Griffin 2003; Ceríaco, Branch & Bauer 2018).
Records from Saudi Arabia and Yemen (Al-Jumaily 1984) refer to
Ablepharus pannonicus (Arnold 1986; Schätti 1989).
Greenbaum, Bauer & Jackman (2007) pointed out that walbergii is the original spelling of the specific epithet, however, Smith corrected this in an addenda slip
(Broadley, Jackman & Bauer 2014).
Distribution:
Angola,
Botswana,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Eswatini,
Ethiopia,
Kenya,
Malawi,
Mozambique
(incl.
Bazaruto Archipelago
[Benguerua]),
Somalia,
South Africa
(Eastern Cape,
Free State,
Gauteng,
KwaZulu-Natal,
Limpopo,
Mpumalanga,
North West Province,
Northern Cape),
Tanzania,
Uganda,
Zambia,
Zimbabwe.
|

|

|
Panaspis wilsoni



 |
Sudan Snake-eyed Skink
|

 |
Sudanisches Natternauge
|

 |
Sudansk Brilleskink
|

|
1914 |  |
Ablepharus wilsoni Werner |
|
|  |
Panaspis wilsoni Fuhn 1970 |
|
|  |
Afroablepharus wilsoni Greer 1974 |

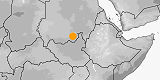
Distribution:
Sudan.
|

|
|