Citation: Midtgaard, Rune. RepFocus - A Survey of the Reptiles of the World. (www.repfocus.dk).
Latest update:
January 31st, 2025.






|
Genus
Atractaspis

 |
Stiletto Snakes, (Stiletto Vipers, Burrowing Asps, Burrowing Vipers, African Mole Vipers)
|

 |
Erdvipern
|

 |
Jordhugorme, Jordvipere
|

|
1849 |  |
Atractaspis Smith (type species: Atractaspis inornatus Smith 1848) |
|
1854 |  |
Brachycranion Hallowell (type species: Brachycranion corpulentum Hallowell 1854) |
|
1862 |  |
Eurystephus Cope (type species: Elaps irregularis Reinhardt 1843) |
|
1906 |  |
Melanelaps Wall (type species: Melanelaps mcphersoni Wall 1906) |
Contents:
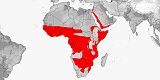
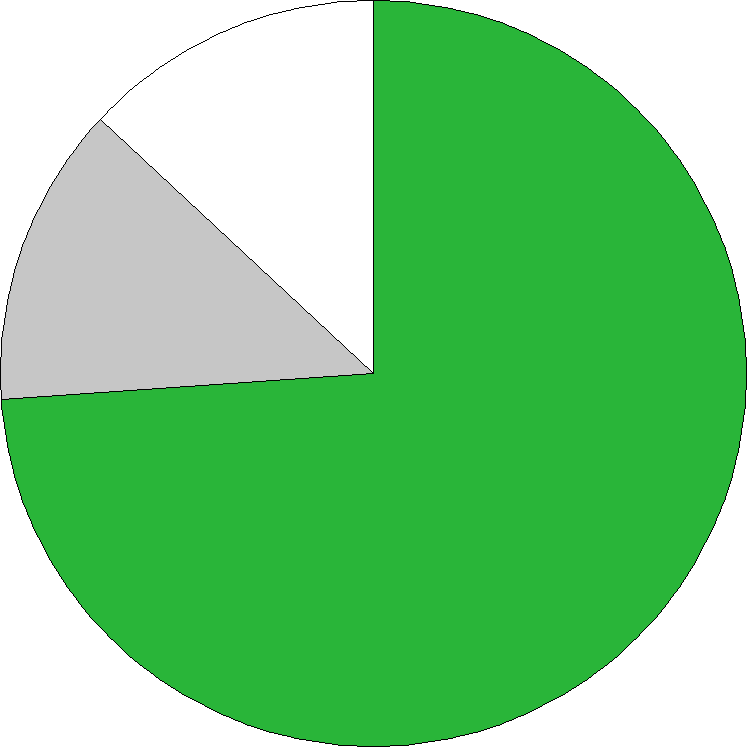
25 species, of which 3 (12.0%) is endemic.
Endemism: 0%  100% 100%
Remarks:
This genus and its related genera have had a turbulent taxonomic history.
Placed in a separate family, Atractaspididae, by Kochva & Meier (1986), followed by some authors (e.g., Ovadia 1987; Broadley 1991; Underwood & Kochva 1993).
It has also been placed in
Colubridae
(e.g., Smith, Smith & Sawin 1977),
Viperidae (e.g., Loveridge 1957),
or
Elapidae (e.g., Lawson, Slowinski, Crother & Burbrink 2005).
Since these snakes are not true vipers, Broadley’s (1983) suggestion of using the common name Stiletto Snakes is followed here.
The type species of Atractaspis is bibronii, not the unavailable name inornatus (David & Ineich 1999).
Introduced to:
New Zealand.
Distribution:
SubSaharan Africa, Middle East.
Reported from:
Angola
(incl.
Cabinda),
Benin,
Botswana,
Burkina Faso,
Burundi,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Chad,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Djibouti,
Egypt
(Sinai),
Equatorial Guinea
(Rio Muni),
Eritrea,
Eswatini,
Ethiopia,
Gabon,
Gambia,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Guinea-Bissau,
Israel,
Ivory Coast,
Jordan,
Kenya,
Liberia,
Malawi,
Mali,
Mauritania,
Mozambique
(incl.
Bazaruto Archipelago
[incl.
Benguerua]),
Namibia,
Niger,
Nigeria,
Oman,
Rwanda,
Saudi Arabia,
Senegal,
Sierra Leone,
Somalia,
South Africa
(Eastern Cape,
Free State,
Gauteng,
KwaZulu-Natal,
Limpopo,
Mpumalanga,
North West Province,
Northern Cape),
South Sudan,
Sudan,
Tanzania
(incl.
Zanzibar),
Togo,
Uganda,
Yemen,
Zambia,
Zimbabwe.
| |

|
Atractaspis andersonii



 |
Arabian Stiletto Snake, (Anderson's Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Arabische Erdviper
|

 |
Arabisk Jordhugorm
|

|
1905 |  |
Atractaspis andersonii Boulenger |
|
|  |
Atractaspis microlepidota andersonii Laurent 1950 |
|
1906 |  |
Melanelaps mcphersoni Wall (Golay & al. 1993) |

Remarks:
Regarded by some authors as a subspecies of microlepidota (Gasperetti 1988; Golay & al. 1993; Gardner 2013), but treated as a separate species by others
(Largen & Rasmussen 1993).
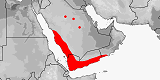
Distribution:
Oman,
Saudi Arabia,
Yemen.
|

|

|
Atractaspis aterrima



 |
Western Forest Stiletto Snake, (Slender Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Schlanke Erdviper
|

 |
Vestlig Jordhugorm
|

|
1863 |  |
Atractaspis aterrima Günther |

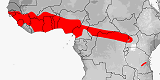
Distribution:
Benin,
Burkina Faso,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Chad,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Gambia,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Guinea-Bissau,
Ivory Coast,
Liberia,
Mali,
Nigeria,
Rwanda,
Senegal,
Sierra Leone,
South Sudan,
Tanzania,
Togo,
Uganda.
|

|

|
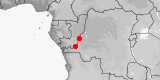
Atractaspis battersbyi



 |
Bolobo Stiletto Snake, (Battersby's Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Bolobo-Erdviper
|

 |
Bolobo-jordhugorm
|

|
1959 |  |
Atractaspis battersbyi Witte |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a synonym of irregularis (e.g., David & Ineich 1999).
Treated as a separate species herein, following Trape (2023).
Distribution:
Congo-Kinshasa.
|

|

|
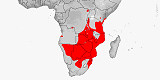
Atractaspis bibronii



 |
Southern Stiletto Snake, (Bibron's Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Bibrons Erdviper
|

 |
Sydlig Jordhugorm
|

|
1849 |  |
Atractaspis bibronii Smith |
|
|  |
Atractaspis irregularis bibronii Boettger 1887 |
|
1848 |  |
Atractaspis inornatus Smith (Golay & al. 1993) |
|
1901 |  |
Atractaspis coarti Boulenger (Golay & al. 1993) |
|
1901 |  |
Atractaspis katangae Boulenger (Golay & al. 1993) |
|
|  |
Atractaspis bibroni katangae Laurent 1945 |

Remarks:
Previously included rostrata.
Distribution:
Angola,
Botswana,
Burundi,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Eswatini,
Kenya,
Malawi,
Mozambique
(incl.
Bazaruto Archipelago
[incl.
Benguerua]),
Namibia,
Rwanda,
Somalia,
South Africa
(Eastern Cape,
Free State,
Gauteng,
KwaZulu-Natal,
Limpopo,
Mpumalanga,
North West Province,
Northern Cape),
Tanzania
(incl.
Zanzibar),
Zambia,
Zimbabwe.
|

|

|
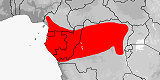
Atractaspis boulengeri



 |
Central African Stiletto Snake, (Boulenger's Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Zentralafrikanische Erdviper
|

 |
Centralafrikansk Jordhugorm
|

|
1897 |  |
Atractaspis boulengeri Mocquard |
|
1897 |  |
Atractaspis matschiensis Werner |
|
|  |
Atractaspis boulengeri matschiensis Laurent 1950 |
|
1917 |  |
Atractaspis schultzei Sternfeld |
|
|  |
Atractaspis boulengeri schultzei Laurent 1950 |
|
1945 |  |
Atractaspis boulengeri mixta Laurent |
|
1945 |  |
Atractaspis boulengeri schmidti Laurent |
|
1956 |  |
Atractaspis boulengeri vanderborghti Laurent |

Remarks:
There are no published records from Angola (Marques, Ceríaco, Blackburn & Bauer 2018), but the species has been listed for the country by several authors
(e.g., Manacas 1981; Spawls & Branch 1995; Dobiey & Vogel 2007).
Distribution:
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Equatorial Guinea
(Rio Muni),
Gabon,
Gambia.
|

|

|
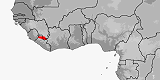
Atractaspis branchi



 |
Liberian Stiletto Snake, (Branch's Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Liberianische Erdviper
|

 |
Liberiansk Jordhugorm
|

|
2019 |  |
Atractaspis branchi Rödel, Kucharzewski, Mahlow, Chirio, Pauwels, Carlino, Sambolah & Glos |

Distribution:
Guinea,
Liberia.
|

|

|
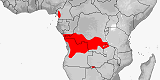
Atractaspis congica



 |
Congo Stiletto Snake
|

 |
Kongo-Erdviper
|

 |
Congolesisk Jordhugorm
|

|
1877 |  |
Atractaspis congica Peters |
|
|  |
Atractaspis irregularis congica Boettger 1887 |
|
1945 |  |
Atractaspis congica orientalis Laurent |

Other common names:
congica: Western Congo Stiletto Snake
orientalis: Eastern Congo Stiletto Snake, Oriental Stiletto Snake
Remarks:
Previously included leleupi.
Distribution:
Angola
(incl.
Cabinda),
Botswana,
Cameroon,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Namibia,
Zambia.
|

|

|
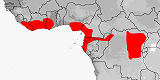
Atractaspis corpulenta



 |
Fat Stiletto Snake, (Hallowell's Stiletto Snake, Corpulent Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Dicke Erdviper
|

 |
Tyk Jordhugorm
|

|
1854 |  |
Brachycranion corpulentum Hallowell |
|
|  |
Atractaspis corpulentus Hallowell 1957 |
|
1885 |  |
Atractaspis leucura Mocquard |
|
|  |
Atractaspis corpulenta leucura Laurent 1950 |
|
1958 |  |
Atractaspis corpulenta kivuensis Laurent |

Other common names:
kivuensis: Kivu Fat Stiletto Snake
leucura: Bright Fat Stiletto Snake
Distribution:
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Equatorial Guinea
(Rio Muni),
Gabon,
Ghana,
Ivory Coast,
Liberia,
Nigeria,
Sierra Leone.
|

|


|
Atractaspis dahomeyensis



 |
Dahomey Stiletto Snake
|

 |
Dahomey-Erdviper
|

 |
Dahomey-jordhugorm
|

|
1887 |  |
Atractaspis dahomeyensis Bocage |
|
1908 |  |
Atractaspis caudalis Sternfeld (Golay & al. 1993) |

Remarks:
Presence in Niger needs confirmation (Trape & Mané 2015).
Records from the Central African Republic (Chippaux 1999; Wallach, Williams & Boundy 2014) are erroneous (Trape, Kodindo, Djiddi, Mad-Toïngué & Kerah 2020).
Distribution:
Benin,
Burkina Faso,
Cameroon,
Chad,
Gambia,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Ivory Coast,
Mali,
Nigeria,
Senegal,
Togo.
|

|

|
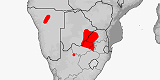
Atractaspis duerdeni



 |
Beaked Stiletto Snake, (Duerden's Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Geschnäbelte Erdviper
|

 |
Næb-jordhugorm
|

|
1907 |  |
Atractaspis duerdeni Gough |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a synonym of bibroni (e.g., Welch 1982).
Distribution:
Botswana,
Namibia,
South Africa
(Gauteng,
Limpopo,
North West Province,
Northern Cape).
|

|

|
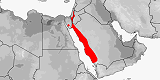
Atractaspis engaddensis



 |
Palestine Stiletto Snake, Black Mole Viper, Israeli Mole Viper, (Ein Gaddi's Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Ein Gaddi-Erdviper
|

 |
Palæstinensisk Jordhugorm
|

|
1950 |  |
Atractaspis engaddensis Haas |
|
|  |
Atractaspis microlepidota engaddensis Leviton & Aldrich 1984 |

Remarks:
Regarded by some authors as a subspecies of microlepidota (Leviton & Aldrich 1984; Gasparetti 1988; Golay & al. 1993), but as a separate species in most recent works (Kochva & Golani 1993, Leviton, Anderson, Adler & Minton 1992, Underwood & Kochva 1993, Werner & Werner 1990; Baha el Din 2006).
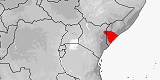
Distribution:
Egypt
(Sinai),
Israel,
Jordan,
Saudi Arabia.
|

|

|
Atractaspis engdahli



 |
Kismayu Stiletto Snake, (Engdahls' Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Engdahls Erdviper
|

 |
Kismayu-jordhugorm
|

|
1913 |  |
Atractaspis engdahli Lönnberg & Andersson |

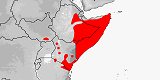
Distribution:
Kenya,
Somalia.
|

|

|
Atractaspis fallax



 |
Eastern Small-scaled Stiletto Snake, (False Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Östliche Kleinschuppige Erdviper, (Falsche Erdviper)
|

 |
Østlig Småskællet Jordhugorm, (Uægte Jordhugorm)
|

|
1866 |  |
Atractaspis fallax Peters |
|
|  |
Atractaspis microlepidota fallax Laurent 1950 |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a subspecies of microlepidota or confused with other taxa.
Revalidated by Hughes (1983) and Largen & Rasmussen (1993).
Davis & Vogel (2010) expressed doubt regarding the validity of phillipsi, suggesting that it might prove to be a synonym of fallax.
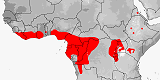
Distribution:
Ethiopia,
Kenya,
Somalia,
Tanzania.
|

|

|
Atractaspis irregularis



 |
Variable Stiletto Snake
|

 |
Bunte Erdviper, Variable Erdviper
|

 |
Broget Jordhugorm
|

|
1843 |  |
Elaps irregularis Reinhardt |
|
|  |
Atractaspis irregularis Boulenger 1896 |
|
1905 |  |
Atractaspis bipostocularis Boulenger |
|
|  |
Atractaspis irregularis bipostocularis Laurent 1950 |
|
1908 |  |
Atractaspis conradsi Sternfeld (Golay & al. 1993) |
|
|  |
Atractaspis irregularis conradsi Laurent 1945 |
|
1930 |  |
Atractaspis schoutedeni Witte (Golay & al. 1993) |
|
1934 |  |
Atractaspis babaulti Angel (Golay & al. 1993) |
|
1945 |  |
Atractaspis irregularis loveridgei Laurent (Golay & al. 1993) |
|
1945 |  |
Atractaspis irregularis parkeri Laurent |
|
1945 |  |
Atractaspis irregularis uelensis Laurent |
|
1950 |  |
Atractaspis irregularis angeli Laurent |
|
1960 |  |
Atractaspis coalescens Perret (David & Ineich 1999; Chirio & LeBreton 2007) |

Other common names:
angeli: Angel's Stiletto Snake
bipostocularis: Eastern Variable Stiletto Snake
coalescens: (Black Stiletto Snake)
parkeri: Parker's Variable Stiletto Snake
uelensis: Uele Variable Stiletto Snake
Remarks:
Previously included battersbyi.
Status of coalescens is uncertain.
Tentatively treated as a synonym of irregularis by David & Ineich (1999) and David & Vogel (2010), but as a separate species by Chippaux & Jackson (2019).
Wallach, Williams & Boundy (2014) listed battersbyi as a valid species.
Reported to occur in the Gambia (Pauwels & Meirte 1996), but its presence there remains unconfirmed,
although possible (Emms, Jambang, Bahl, Mankali, Paziaud & Barnett 2007).
Branch (2018) did not mention this species for Angola, in spite of numerous records.
Introduced to:
New Zealand.
Distribution:
Angola
(incl.
Cabinda),
Burundi,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Eritrea,
Ethiopia,
Ghana,
Guinea,
Ivory Coast,
Kenya,
Liberia,
Nigeria,
Rwanda,
Sierra Leone,
South Sudan,
Tanzania,
Togo,
Uganda.
|

|


|
Atractaspis katangae



 |
Katanga Stiletto Snake
|

 |
Katanga-Erdviper
|

 |
Katanga-jordhugorm
|

|
1901 |  |
Atractaspis katangae Boulenger |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a synonym of bibronii (e.g., Laurent 1945).
Revalidated as a separate species by Trape & Collet (2021).
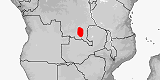
Distribution:
(under revision):
Congo-Kinshasa.
|

|

|
Atractaspis leleupi



 |
Kundelungu Stiletto Snake, (Leleup's Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Kundelungu-Erdviper, (Leleups Erdviper)
|

 |
Kundelungu-jordhugorm
|

|
1950 |  |
Atractaspis congica leleupi Laurent |
|
|  |
Atractaspis leleupi Broadley & Cotterill 2004 |

Distribution:
Congo-Kinshasa.
|

|

|
Atractaspis leucomelas


 |
Ogaden Stiletto Snake
|

 |
Schwarzweisse Erdviper
|

 |
Ogaden-jordhugorm
|

|
1895 |  |
Atractaspis leucomelas Boulenger |

Remarks:
Although reported to occur in Djibouti by some authors (Spawls & Branch 1995; David & Ineich 1999; Wallach, Williams & Boundy 2014), the species was not listed for the country by Nistri & Vanni (2014).
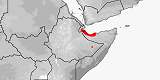
Distribution:
Djibouti,
Ethiopia,
Somalia.
|

|

|
Atractaspis magrettii



 |
Mandafená Stiletto Snake, (Magretti's Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Magrettis Erdviper
|

 |
Mandafena-jordhugorm
|

|
1928 |  |
Atractaspis magrettii Scortecci |
|
|  |
Atractaspis microlepidota magrettii Scortecci 1939 |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a subspecies of microlepidota, but treated as a separate species in most recent works
(e.g., Largen & Rasmussen 1993; David & Ineich 1999).
It has also been suggested that magrettii represents a distinct African population of the Arabian species andersoni (Largen & Rasmussen 1993).
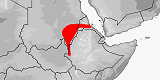
Distribution:
Eritrea,
Ethiopia,
Somalia,
Sudan.
|

|

|
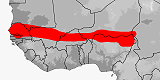
Atractaspis microlepidota



 |
Western Small-scaled Stiletto Snake, (Black Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Westliche Kleinschuppige Erdviper
|

 |
Vestlig Småskællet Jordhugorm
|

|
1866 |  |
Atractaspis microlepidota Günther |

Remarks:
Now restricted to Gambia, Mauritania, and Senegal (Trape 2005; Trape & Mané 2006). Previously regarded as a polytypic species with six subspecies (microlepidota, andersonii, engaddensis, fallax, magretti, micropholis), all of which are now regarded as full species. Records from Central African Republic refer to watsoni (Chirio & Ineich 2006).
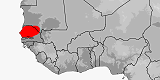
Distribution:
Gambia,
Mauritania,
Senegal.
|

|

|
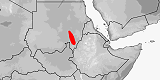
Atractaspis micropholis



 |
Sahelian Stiletto Snake, Common Stiletto Snake
|

 |
Gewöhnliche Erdviper
|

 |
Sahel-jordhugorm
|

|
1872 |  |
Atractaspis micropholis Günther |
|
|  |
Atractaspis microlepidota micropholis Laurent 1950 |
|
1909 |  |
Atractaspis nigra Pellegrin (Golay & al. 1993) |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a subspecies of microlepidota. Revalidated as a separate species by Trape & Mané (2000), although other authors before them had already regarded it as such (e.g., Hughes 1983; Wallach 1991). Previously included watsoni. Records from Burkina Faso refer to watsoni (Trape 2005).
Distribution:
Burkina Faso,
Chad,
Gambia,
Mali,
Mauritania,
Niger,
Nigeria,
Senegal.
|

|

|
Atractaspis phillipsi


 |
Sudanese Stiletto Snake, (Phillips' Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Phillips' Erdviper
|

 |
Sudansk Jordhugorm
|

|
1913 |  |
Atractaspis phillipsi Barbour |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a synonym of microlepidota (e.g., Laurent 1950; Largen & Rasmussen 1993). Revalidated by Golay, Smith, Broadley, Dixon, McCarthy, Rage, Schätti & Toriba (1993) and Broadley (1994). Davis & Vogel (2010) expressed doubt regarding the validity of phillipsi, suggesting that it might prove to be a synonym of fallax.
Distribution:
Ethiopia,
South Sudan,
Sudan.
|

|

|
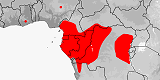
Atractaspis reticulata



 |
Reticulate Stiletto Snake
|

 |
Netz-Erdviper
|

 |
Net-jordhugorm
|

|
1896 |  |
Atractaspis reticulata Sjostedt |
|
1901 |  |
Atractaspis heterochilus Boulenger |
|
|  |
Atractaspis reticulata heterochilus Laurent 1950 |
|
1956 |  |
Atractaspis reticulata brieni Laurent |

Other common names:
brieni: Brien's Reticulate Stiletto Snake
heterochilus: Boulenger's Reticulate Stiletto Snake
Distribution:
Angola
(incl.
Cabinda),
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Congo-Brazzaville,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Equatorial Guinea
(Rio Muni),
Gabon,
Ghana,
Nigeria.
|

|


|
Atractaspis rostrata



 |
Zanzibar Stiletto Snake
|

 |
Zanzibar-Erdviper
|

 |
Zanzibar-jordhugorm
|

|
1868 |  |
Atractaspis rostrata Günther |
|
|  |
Atractaspis bibroni rostrata Laurent 1950 |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a subspecies of bibronii (e.g., Laurent 1950; Broadley & Howell 1991).
Treated as a separate species herein, following Trape (2023).
Distribution:
Angola,
Burundi,
Congo-Kinshasa,
Kenya,
Malawi,
Mozambique,
Rwanda,
Tanzania
(incl.
Zanzibar).
|

|

|
Atractaspis scorteccii


 |
Somali Stiletto Snake
|

 |
Somali-Erdviper
|

 |
Somalisk Jordhugorm
|

|
1949 |  |
Atractaspis scorteccii Parker |

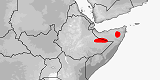
Distribution:
Ethiopia,
Somalia.
|

|

|
Atractaspis watsoni



 |
Sokoto Stiletto Snake, (Watson's Stiletto Snake)
|

 |
Sokoto-Erdviper, (Watsons Erdviper)
|

 |
Sokoto-jordhugorm
|

|
1908 |  |
Atractaspis watsoni Boulenger |

Remarks:
Previously regarded as a synonym of micropholis (e.g., Laurent 1950; Golay & al. 1993). Revalidated by Trape, Mané & Ineich (2006).
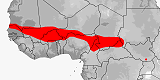
Distribution:
Benin,
Burkina Faso,
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Chad,
Eritrea,
Mali,
Mauritania,
Niger,
Nigeria,
South Sudan,
Sudan.
|

|
|